Recognizing Speech¶
The recognizer allows users to speak instead of type in locations where text entry would generally be required. The speech recognizer returns a list of text results. It is not attached to any UI object in any way, so the presentation of the best result and selection of alternative results is left up to the UI of application.
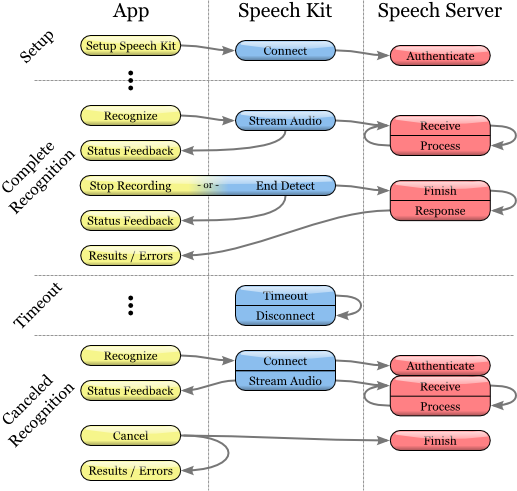
Speech Recognition Process
Initiating a Recognition¶
Before you use speech recognition, ensure that you have set up the core Speech Kit library with the SpeechKit.initialize method.
Then create and initialize a Recognizer object:
recognizer = sk.createRecognizer(Recognizer.RecognizerType.Dictation, Recognizer.EndOfSpeechDetection.Short, "en_US", this, handler);
The SpeechKit.createRecognizer method initializes a recognizer and starts the speech recognition process.
The type parameter is a String, generally one of the recognition type constants defined in the Speech Kit library and available in the class documentation for Recognizer. Nuance may provide you with a different value for your unique recognition needs, in which case you will enter the raw String.
The detection parameter determines the end-of-speech detection model and must be one of the Recognizer.EndOfSpeechDetection types.
The language parameter defines the speech language as a string in the format of the ISO 639 language code, followed by an underscore “_”, followed by the ISO 3166-1 country code.
Note
For example, the English language as spoken in the United States is en_US. An up-to-date list of supported languages for recognition is available on the FAQ at http://nuancemobiledeveloper.com/public/index.php?task=faq.
The this parameter defines the object to receive status, error, and result messages from the recognizer. It can be replaced with any object that implements the RecognizerListener interface.
handler should be an android.os.Handler object that was created with
Handler handler = new Handler();
Handler is a special Android object that processes messages. It is needed to receive call-backs from the Speech Kit library. This object can be created inside an Activity that is associated with the main window of your application, or with the windows or controls where voice recognition will actually be used.
Start the recognition by calling start.
The Recognizer.Listener passed into SpeechKit.createRecognizer receives the recognition results or error messages, as described below.
Using Prompts¶
Prompts are short audio clips or vibrations that are played during a recognition. Prompts may be played at the following stages of the recognition:
- Recording start: the prompt is played before recording. The moment the prompt completes, recording will begin.
- Recording stop: the prompt is played when the recorder is stopped.
- Result: the prompt is played if a successful result is received.
- Error: the prompt is played if an error occurs.
The SpeechKit.defineAudioPrompt method defines an audio prompt from a raw resource ID packaged with the Android application. Audio prompts may consume significant system resources until release is called, to try to minimize the number of instances. The Prompt.vibrate method defines a vibration prompt. Vibration prompts are inexpensive–they can be created on the fly as they are used, and there is no need to release them.
Call SpeechKit.setDefaultRecognizerPrompts to specify default audio or vibration prompts to play during all recognitions by default. To override the default prompts in a specific recognition, call setPrompt prior to calling start.
Receiving Recognition Results¶
To retrieve the recognition results, implement the Recognizer.Listener.onResults method. For example:
public void onResults(Recognizer recognizer, Recognition results) {
String topResult;
if (results.getResultCount() > 0) {
topResult = results.getResult(0).getText();
// do something with topResult...
}
}
This method will be called only on successful completion, and the results list will have zero or more results.
Even in the absence of an error, there may be a suggestion, present in the recognition results object, from the speech server. This suggestion should be presented to the user.
Handling Errors¶
To be informed of any recognition errors, implement the onError method of the Recognizer.Listener interface. In the case of errors, only this method will be called; conversely, on success this method will not be called. In addition to the error, a suggestion, as described in the previous section, may or may not be present. Note that both the Recognition and the SpeechError class have a getSuggestion method that can be used to check for a suggestion from the server.
public void onError(Recognizer recognizer, SpeechError error) {
// Inform the user of the error and suggestion
}
Managing Recording State Changes¶
Optionally, to be informed when the recognizer starts or stops recording audio, implement the onRecordingBegin and onRecordingDone methods of the Recognizer.Listener interface. There may be a delay between initialization of the recognizer and the actual start of recording, so the onRecordingBegin message can be used to signal to the user when the system is listening.
public void onRecordingBegin(Recognizer recognizer) {
// Update the UI to indicate the system is now recording
}
The onRecordingDone message is sent before the speech server has finished receiving and processing the audio, and therefore before the result is available.
public void onRecordingDone(Recognizer recognizer) {
// Update the UI to indicate that recording has stopped and the speech is still being processed
}
This message is sent both with and without end-of-speech detection models in place. The message is sent regardless, whether recording was stopped due to calling the stopRecording method or due to detecting end-of-speech.
Power Level Feedback¶
In some scenarios, especially for longer dictations, it is useful to provide a user with visual feedback of the volume of their speech. The Recognizer interface supports this feature by use of the method getAudioLevel, which returns the relative power level of the recorded audio in decibels. The range of this value is a float between 0.0 and -90.0 dB where 0.0 is the highest power level and -90.0 is the lowest level. This method should be accessed during recordings, specifically in the time between receiving the messages onRecordingBegin and onRecordingDone. Generally, you should use a timer method to read the power level regularly.