Converting Text to Speech¶
The Vocalizer class provides a network text-to-speech interface for developers.
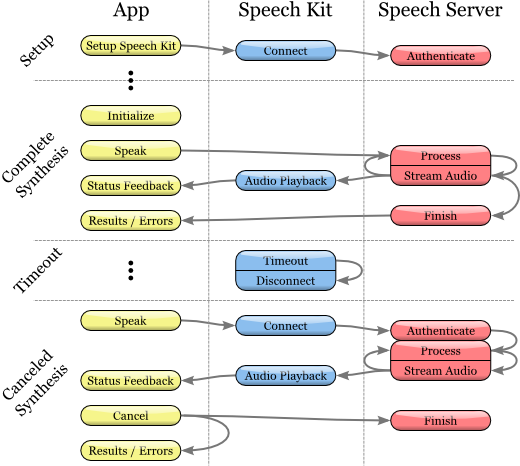
Text-to-Speech Process
Initiating Text-To-Speech¶
Before you use speech synthesis, ensure that you have setup the core Speech Kit library with the SpeechKit.initialize method.
Then create and initialize a Vocalizer object to perform text-to-speech conversion:
Vocalizer voc = sk.createVocalizerWithLanguage("en_US", this, handler);
The Vocalizer.createVocalizerWithLanguage method initializes a text-to-speech synthesizer with a default language.
The language parameter is a String that defines the spoken language in the format of the ISO 639 language code, followed by an underscore “_”, followed by the ISO 3166-1 country code. For example, the English language as spoken in the United States is en_US. Each supported language has one or more uniquely defined voices, either male or female.
Note
An up-to-date list of supported languages for text-to-speech is available at http://nuancemobiledeveloper.com/public/index.php?task=faq. The list of supported languages will be updated when new language support is added. The new languages will not necessarily require updating an existing Dragon Mobile SDK.
The this parameter defines the object to receive status and error messages from the speech synthesizer. It can be replaced with any object that implements the Vocalizer.Listener interface.
handler should be an android.os.Handler object that was created with
Handler handler = new Handler();
Handler is a special Android object that processes messages. It is needed to receive call-backs from the Speech Kit library. This object can be created inside an Activity that is associated with the main window of your application, or with the windows or controls where Text-To-Speech will actually be used.
The Vocalizer.createVocalizerWithLanguage method uses a default voice chosen by Nuance. To select a different voice, use the createVocalizerWithVoice method instead.
The voice parameter is a String that defines the voice model. For example, the female US English voice is Samantha.
Note
The up-to-date list of supported voices is provided with the supported languages at http://nuancemobiledeveloper.com/public/index.php?task=faq.
To begin converting text to speech, you must use either the speakString or speakMarkupString method. These methods send the requested string to the speech server and start streaming and playing audio on the device.
voc.speakString("Hello world.", context);
Note
The speakMarkupString method is used in exactly the same manner as speakString except that it takes a String filled with SSML, a markup language tailored for use in describing synthesized speech. An advanced discussion of SSML is beyond the scope of this document, however you can find more information from the W3C at http://www.w3.org/TR/speech-synthesis/.
As speech synthesis is a network-based service, these methods are all asynchronous, and in general an error condition is not immediately reported. Any errors are reported as messages to the Vocalizer.Listener that was passed to createVocalizerWithLanguage or createVocalizerWithVoice.
The speakString and speakMarkupString methods may be called multiple times for a single Vocalizer instance. To change the language or voice without having to create a new Vocalizer, call setLanguage or setVoice.
Managing Text-To-Speech Feedback¶
The synthesized speech will not immediately start playback. Rather there will be a brief delay as the request is sent to the speech server and speech is streamed back. For UI coordination, to indicate when audio playback begins, the optional method Vocalizer.Listener.onSpeakingBegin is provided.
public void onSpeakingBegin(Vocalizer vocalizer, String text, Object context) {
// update UI to indicate that text is being spoken
}
The context in the message is a reference to the context that was passed to one of the speakString or speakMarkupString methods and may be used track sequences of playback when sequential text-to-speech requests are made.
On completion of the speech playback, the Vocalizer.Listener.onSpeakingDone message is sent. This message is always sent on successful completion and on error. In the success case, error is null.
public void onSpeakingDone(Vocalizer vocalizer, String text, SpeechError error, Object context) {
if (error != null) {
// Present error dialog to user
} else {
// Update UI to indicate speech is complete
}
}